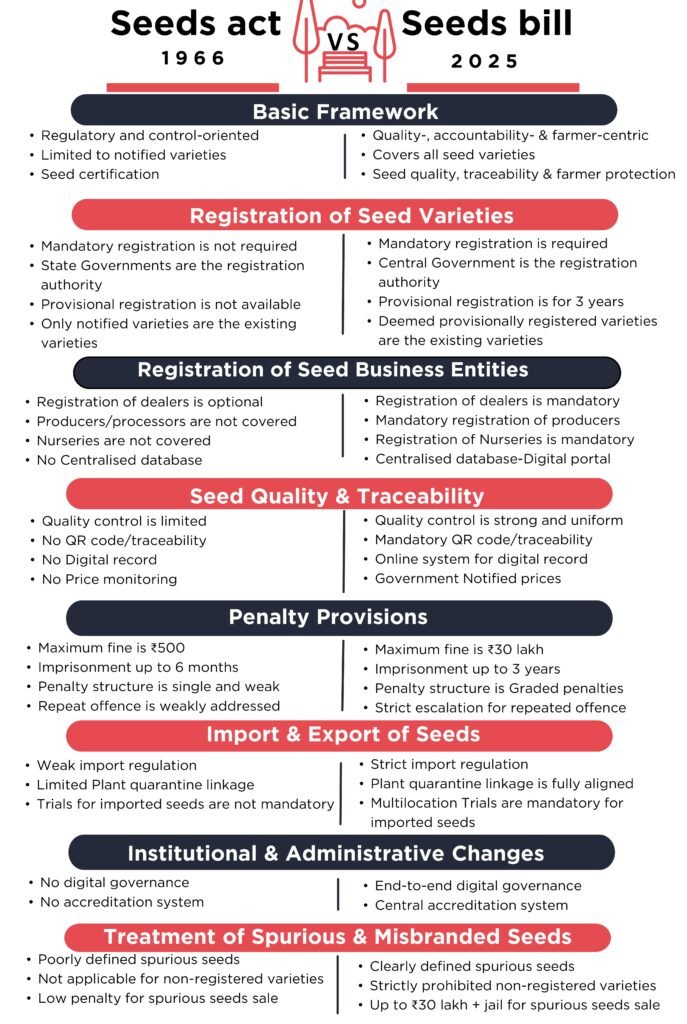
Quality seeds are the foundation of agriculture. Yet, farmers often suffer due to fake, sub-standard, or misbranded seeds. To address these long-standing issues and modernise seed regulation, the Government of India has introduced the Seeds Bill, 2025. This new law replaces the outdated Seeds Act, 1966, and brings transparency, accountability, and farmer protection into the seed system. Let’s break down what Draft Seeds Bill-2025 is in simple words.

CHAPTER I – Preliminary
1. Short title & commencement
Called Seeds Act, 2025
Applies to:
Seed producers,
Seed processors,
Dealers & distributors, and
Importers & exporters
Comes into force on dates notified by the Central Government
Farmer Rights
Farmers can:
- Grow, sow, re-sow
- Save, use, exchange, share
- Sell seeds without branding
Farmers cannot sell branded seeds
Key Definitions
Seed: Includes grains, seedlings, tubers, grafts, tissue culture plants, etc.
Variety: A plant type with specific genetic traits
Misbranded seed: False or misleading label
Spurious seed: Not genetically pure or true to type
Sub-standard seed: Does not meet germination/purity standards
Farmer: One who cultivates crops (not seed traders)
Producer: Organises seed production (not farmers)
Dealer/Distributor: Sells or stocks seeds
Seed processing: Cleaning, grading, treating seeds
Plant nursery: Produces plants for sale
CHAPTER II – Committees
Central Seed Committee (CSC)
- Headquartered in New Delhi
- Chairperson + 27 members
Advises on:
- Seed policy
- Registration
- Import/export
- Standards & certification
Registration Sub-Committees
- Examine seed varieties
- Recommend approval or rejection
State Seed Committee
- Formed by every State
Maintains lists of:
- Seed producers
- Dealers & distributors
- Nurseries
- Advises State Governments
CHAPTER III – Registration of Seed Varieties
National Register on Seed Varieties
- All registered varieties listed here
- Mandatory Registration
- No seed can be sold for sowing unless registered
- Exceptions: Farmers’ varieties and seeds produced only for export
Registration Process
- Submission of Application submitted
- Multi-location trials (VCU – Value for Cultivation & Use)
Evaluation of:
- Performance
- Safety to humans, animals & environment
Suspension / Cancellation
Registration can be cancelled if:
- False data was given
- Variety fails in performance
- Harmful to health or environment
- Becomes obsolete
CHAPTER IV – Registration of Seed Businesses
Mandatory Registration For:
- Seed producers
- Seed processing units
- Dealers & distributors
- Plant nurseries
Seed Producers & Processing Units
- Registered by State Government
- Must have:
- Infrastructure
- Equipment
- Skilled manpower
- Must maintain records
Central Accreditation System
- Companies working in many States get central accreditation
- Automatically valid across States
- Improves ease of doing business
Plant Nurseries
- Must be registered
- Must maintain:
- Mother plant records
- Source of planting material
- Disease-free plants
- Small nurseries may be exempted
CHAPTER V – Sale of Seeds & Certification
Conditions for Selling Seeds
Seeds must:
- Be registered
- Meet minimum standards:
- Germination
- Genetic & physical purity
- Seed health
- Carry:
- Proper label
- QR Code linked to Seed Traceability Portal
- Sale of misbranded seeds is banned
Seed Price Control
- Government can regulate seed prices during:
- Shortages
- Price rise
- Hoarding or profiteering
Seed Certification Agencies
- Set up by States
- Can be:
- Government
- Accredited private bodies
- Certify seed quality
- Certification can be withdrawn if rules are violated
- Foreign certification agencies can be recognised
CHAPTER VI – Review & Appeals
Decisions can be:
- Reviewed (only once)
- Appealed against
- Appeal authorities set by Government
- Ensures natural justice
CHAPTER VII – Seed Testing & Inspection
Seed Testing Laboratories
- Central & State Seed Testing Labs
- Follow prescribed standards
Seed Analysts
- Test seed samples
- Submit official reports
Seed Inspectors
- Can:
- Take seed samples
- Inspect premises
- Seize stocks
- Check records
- Stop sale temporarily up to 15 days
- Legal procedure according to Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023
Import of Seeds
- Allowed only if:
- Registered
- Meets Indian standards
- Proper testing & certification done
Penalty Provisions under Seeds Bill, 2025
Penalties are categorised into 3 levels
- Trivial Offences (Schedule 2 – Part A)
- Penalty:
- Warning for first offence
- ₹50,000 for repeat offence (within 3 years)
- Examples:
- Not displaying registration certificate
- Missing QR code
- No label on seed packet
- Business on expired registration (last 12 months)
- Minor Offences (Schedule 2 – Part B)
- Penalty:
- ₹1 lakh
- ₹2 lakh if repeated within 3 years
- Examples:
- Selling misbranded seeds
- Selling sub-standard seeds
- Selling above government-fixed price
- Not uploading details on traceability portal
- Major Offences (Schedule 2 – Part C)
- Penalty:
- ₹10 lakh-first offence
- ₹20 lakh-second offence (within 5 years)
- ₹30 lakh + cancellation of licence OR imprisonment up to 3 years-third offence
- Examples:
- Selling spurious seeds
- Selling non-registered varieties
- Seed business without registration
Important Time Limits
| Activity | Time Period |
| Submission of list of existing varieties | 6 months |
| Provisional registration validity | 3 years |
| Appeal filing period | 30 days |
| Review of decision | Only once |
| Suspension of sale by Seed Inspector | Up to 15 days |
Millet-Based Agroforestry: A Nature-Positive Farming for a Better Future

